Detect Browser Bars Visibility with JavaScript
It's one thing to know about what's in the browser document, it's another to have insight as to the user's browser itself. We've gotten past detecting which browser the user is using, and we're now into knowing what pieces of the browser UI users are seeing.
Browsers provide window.personalbar, window.locationbar, and window.menubar properties, with the shape of { visible : /*boolean*/} as its value:
if(window.personalbar.visible || window.locationbar.visible || window.menubar.visible) {
console.log("Please hide your personal, location, and menubar for maximum screen space");
}
What would you use these properties for? Maybe providing a warning to users when your web app required maximum browser space. Outside of that, these properties seem invasive. What do you think?
![Serving Fonts from CDN]()
For maximum performance, we all know we must put our assets on CDN (another domain). Along with those assets are custom web fonts. Unfortunately custom web fonts via CDN (or any cross-domain font request) don't work in Firefox or Internet Explorer (correctly so, by spec) though...
![6 Things You Didn’t Know About Firefox OS]()
Firefox OS is all over the tech news and for good reason: Mozilla's finally given web developers the platform that they need to create apps the way they've been creating them for years -- with CSS, HTML, and JavaScript. Firefox OS has been rapidly improving...
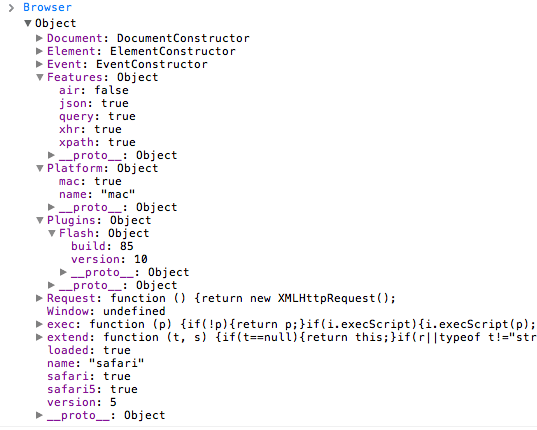
![MooTools 1.3 Browser Object]()
MooTools 1.3 was just released and one of the big additions is the Browser object. The Browser object is very helpful in that not only do you get information about browser type and browser versions, you can gain information about the user's OS, browser plugins, and...
![spellcheck Attribute]()
Many useful attributes have been provided to web developers recently: download, placeholder, autofocus, and more. One helpful older attribute is the spellcheck attribute which allows developers to control an elements ability to be spell checked or subject to grammar checks. Simple enough, right?




I remember testing these out recently, and from memory, they don’t really do anything in most browsers (always set to true).